Information security means protecting information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification, perusal, inspection, recording or destruction (definition from Wikipedia).
The main components
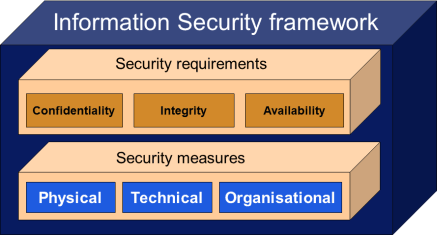
The three classical components in information security are:
- Confidentiality: the guarantee that information is not disclosed to unauthorized individuals or systems.
- Integrity: the guarantee that data is according the reality in terms of correct, timely and complete.
- Availability: the guarantee that data can be accessed at the time and place as required by the data owner.
- Controllability: the ability to check if data presented is correct. Correct here means calculated according to specifications and as a verifiable result of the data inputted.
- Non-repudiation: the existence of evidence that communicating partners have sent and received the information concerned.
If your ambition is to formalise information security, Rominco will perform the gap analyses and propose just those steps that are required to lean and mean implement information security for your organization. The process to be implemented (or formalised) will include those activities required to maintain the level of information security that you aspire.
Common products
In organizations that have implemented information security, a number of products commonly exist. These products are defined below. This list is not exhaustive for any given situation, nor does this list mean that if your organization does not have all products, the level of information security is below par.
Common technical products: network and workstation firewalls, antivirus, anti-malware, anti-spam, identity management provision, authentication software (regularly including self service functionality for blocked or forgotten passwords), intrusion prevention and intrusion protection, server certificates, backup and restore tools, patch distribution, virtual private network solution). Large and/or more mature organizations will have a log file analyses solution in place, to be able to track and investigate doubtful transactions.
Organizational: policy document mainly stating the responsibilities and 5 plus/minus 2 main principles regarding information security, risk analyses including final conclusion, security architecture, information security process including security incident procedure, security plan (including schedule and cost of measures to be implemented), policy on conditions to connect devices to the network, ICT rules of conduct (describing expected user behaviour), communication campaign, information security annual report and business continuity plan. Larger and more mature organizations commonly have audit reports stating the quality of information security. These reports are legally required for financial and health care institutions.
Outsourcing privacy sensitive data
Once you have determined that a service provider offers you the functionality and level of integrity and availability that you require, you can outsource storage and processing if the following requirements are met:
- The services are delivered based on a formal contract;
- The contract has a sound information security section;
- Responsibilities are clearly agreed upon. For instance: who informs who about incidents, who is responsible for solving which disturbances, who monitors the Service Level Agreement on you behalf;
- You have sufficient confidence in the quality of information security offered;
- Legislation of the location where your data will be stored matches the level of privacy that is acceptable for your organization.

